Varicella (Chickenpox)
A very contagious disease that results in blisters when scratched
Overview
Chickenpox, also called varicella, is a very contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is part of the herpes virus family.
It spreads mostly through close contact with someone who has chickenpox, especially if the person has never had it or hasn’t been vaccinated. The virus can spread when someone touches or breathes in particles from the blisters, like when they are scratched.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
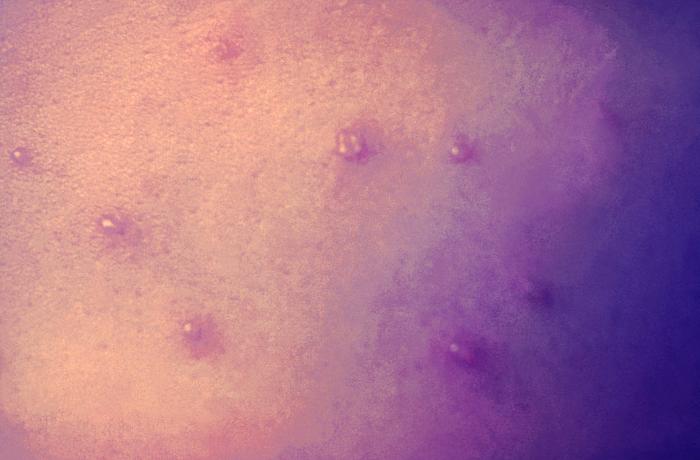
Symptoms of chickenpox usually show up 14 and 16 days after exposure but can appear anytime between 10 and 21 days. Early symptoms include fever, tiredness, loss of appetite, and headache. A rash follows, turning into itchy, fluid-filled blisters that spread over the body. The rash can show up on the scalp, armpits, eyelids, and inside the mouth. The blisters dry out, crust over, and form scabs over time.
Chickenpox can spread 1 to 2 days before an infected person gets the rash, then stays contagious until all the blisters have formed scabs. Vaccinated people who develop breakthrough chickenpox may develop lesions that do not form scabs. These people are considered contagious until no new lesions have appeared for 24 hours.
Those who suspect they might have chickenpox should contact their health care provider, who can advise you on treatment options.
Treatment
Treatment is usually focused on relieving symptoms and preventing skin infections while letting the disease run its course. Calamine lotion and a cool bath with added baking soda, uncooked oatmeal, or colloidal oatmeal may help relieve itching.
Keep fingernails short and minimize scratching to prevent the virus from spreading and to help prevent skin infections. If you do scratch a blister by accident, wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
Do not use aspirin or aspirin-containing products to relieve fever. The use of aspirin in children with chickenpox has been associated with Reye’s syndrome, a severe disease that affects the liver and brain and can cause death. Instead, use non-aspirin medications, such as acetaminophen, to relieve fever from chickenpox.
The American Academy of Pediatrics also recommends avoiding ibuprofen because it has been associated with life-threatening bacterial skin infections.
Prevention
Youth: The CDC recommends two chickenpox vaccine doses: at 12-15 months and 4-6 years. Alaska requires this to enter Kindergarten through sixth grade.
Adults: After chickenpox, the virus can reactivate as shingles. The CDC advises two Shingrix doses for adults 50+ and those 19+ with weakened immune systems.
To prevent spread of infection: Infected individuals should isolate until all lesions dry and crust (usually 5 days for non-immunized people).
Reporting
Health care providers and laboratories are not required to report varicella unless there is a public health risk or outbreak.
Health care providers and laboratories are required to report Varicella-related deaths within two working days.
Learn more about reportable conditions